Migraine and osteopathy
Migraine is usually managed with medication, but some patients do not tolerate it due to side effects or contraindications due to comorbidity. Others wish to avoid them for other reasons. Non-pharmacological management is an alternative treatment option.
Randomized clinical trials (RCTs) of manual migraine therapies may be just as effective as propranolol and topiramate in the prophylactic management of migraine. Thus, massage, physiotherapy and osteopathy can be an alternative treatment option.
Symptoms of migraine

- Only on one side, the right or the left
- Who evolves by crisis
- That changes with each event and can last up to 72 hours if left untreated
- The migraine is pulsatile, meaning that you can feel your heart beating in your head
- The pain increases during physical activity
- This pain can be accompanied by nausea or vomiting
- You become more sensitive to light or noise
5 common causes of migraines
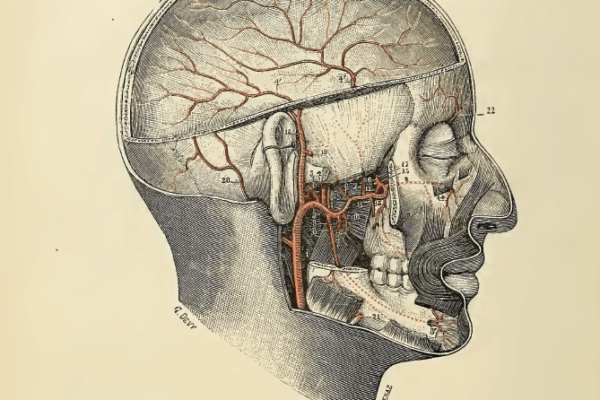
Biomechanical cause
You can suffer from a migraine following a severe trauma such as a car accident, a concussion, or a fall from a bicycle.
This, or these traumas create muscular, joint or skeletal biomechanical tensions in the regions of the spine or skull.
These biomechanical tensions are equally found in osteopathy after a series of wrong moves, poor posture, poor ergonomics that can in the long-term cause you to have recurring migraines.
Nervous cause
This is the case in occipital neuralgia, which, if it is pinched, will create a burning sensation or electric discharges that go from the nape of the neck to the top of the skull and sometimes to the eye.
Other nerve compressions can also be found in the origin of neurological migraines such as:
- Great auricular neuralgia
- Neuralgia of the lesser occipital nerve
Biochemical cause
In women, menstruation can bring on head pains due to hormonal changes, most notably in response to a lowering of oestrogen levels and/or tensions in the lower pelvic organs (via the fasciae).
Vascular cause
This cause is linked to a reduction in intra-cranial circulation of blood. Remember that the arteries and veins play an important role in the distribution of oxygen and the nutrients necessary for proper functioning of the organism.
Ophtalmic cause
In this case there are visual symptoms that appear first and foremost. There is usually a spot of light that slowly gets bigger and occurs in both eyes. This can last for anywhere between 10 minutes and a half-hour.
Osteopathic treatment
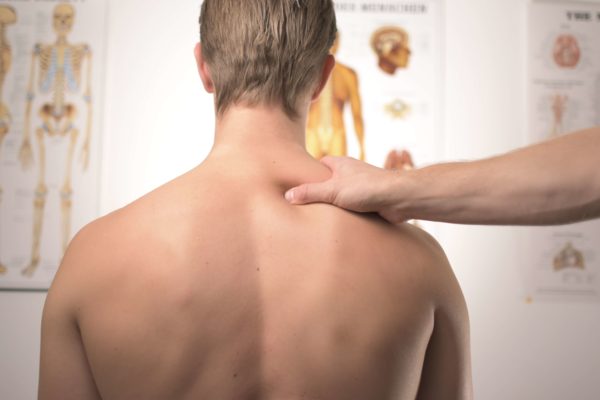
Osteopathy is used to treat the patient in a holistic manner, that is, globally. This takes into account the symptoms evoked by each individual and adds to this the results of a manual examination to propose an optimal therapy that is customized to the patient.
The aim of the treatment, if it is complete and well done, is to avoid recurrence or to increase the period of time between events.
For migraines, a belief that was handed down from the founder of osteopathy, Andrew Taylor Still applies “The Rule of the Artery is Supreme”. In fact, migraines are generally linked to defective cranial vascularization. The intention is therefore to reset the circulation at the level of the various arteries by various methods.
The treatment can also be multidisciplinary with the intervention of another discipline to best optimise treatment; notably the neurologist or the orthoptist.
References
Manual therapies for migraine: a systematic review
Current randomize clinical trials suggest that massage therapy, physiotherapy, relaxation and chiropractic spinal manipulative therapy might be equally efficient as propranolol and topiramate in the prophylactic management of migraine.
Effects of a Physical Therapy Protocol in Patients with Chronic Migraine and Temporomandibular Disorders: A Randomized, Single-Blinded, Clinical Trial.
Both groups reported a significant improvement in CF-PDI, HIT-6, and pain intensity.
Effectiveness of mobilisation of the upper cervical region and craniocervical flexor training on orofacial pain, mandibular function and headache in women with TMD. A randomised, controlled trial.
Women with temporo mandibular disorders reported a significant decrease in orofacial pain and headache impact after 5 weeks of treatment aimed at the upper cervical spine compared to a control group
NOTE: The information contained in this sheet is provided for your information only. Under no circumstances can they replace a consultation.






